-
Intermittent Fasting
References: – www.leangains.com
-
Do You Need To Eat Every 2 Hours
References: i. Schoenfeld BJ Effects of meal frequency on weight loss and body composition: a meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. 2015 Feb;73(2):69-82 ii. Munsters MJM, Saris WHM (2012) Effects of Meal Frequency on Metabolic…
-
LOW CARB Dieting
References: i. Wu H, Wylie-Rosett J, Qi Q. Dietary Interventions for Weight Loss and Maintenance: Preference or Genetic Personalization? Curr Nutr Rep. 2013 Dec;2(4):189-98. ii. Manninen AH. Is a calorie really a…
-
GOOD Vs BAD Fats
References: i. Robert A. Robergs,1 Farzenah Ghiasvand, Biochemistry of exercise-induced metabolic acidosis Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287: R502-R516, 2004; 10.1152/ajpregu.00114.2004.
-
How MANY Meals Should You EAT
References: i. Schoenfeld BJ Effects of meal frequency on weight loss and body composition: a meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. 2015 Feb;73(2):69-82 ii. Munsters MJM, Saris WHM (2012) Effects of Meal Frequency on Metabolic…
-
What a BALANCED Diet can look like
References: a. Gibson SA. Dietary sugars intake and micronutrient adequacy: a systematic review of the evidence. Nutr Res Rev. 2007 Dec;20(2):121-31. b. Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes…
-
Do High Protein Intakes Cause Health Issues
References: Effect of short-term high-protein compared with normal-protein diets on renal hemodynamics and associated variables in healthy young men. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;90:1509–16 Is Increased Dietary Protein Necessary or Beneficial for…
-
Alcohol & Fat Loss
References: Anne Raben, Meals with similar energy densities but rich in protein, fat, carbohydrate, or alcohol have different effects on energy expenditure and substrate metabolism but not on appetite and energy intake…
-
3 BENEFITS to Protein:
References: Cuthbertson D et. al. Anabolic signaling deficits underlie amino acid resistance of wasting, aging muscle. FASEB J. (2005) 19(3):422-4. Tipton KD et. al. Nonessential amino acids are not necessary to stimulate…
-
Macronutrients
Reference: – Andrea C, Is a calorie a calorie? Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79(suppl):899S–906S.
-
Flexible Dieting
References: Tiffany M. Stewart, Donald A.Williamson and Marney A.White Rigid vs. flexible dieting: association with eating disorder symptoms in nonobese women Appetite (2002) QV, 39±44 doi:10.1006/appe.2001.0445 Joachim Westenhoefer Cognitive and weight-related correlates…
-
HOW we BURN Calories
References: – Non-exercise activity thermogenesis – liberating the life-force. J. A. Levine, Endocrine Research Unit, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, US
-
Does the TYPE of Food matter?
References: Johnston CS Postprandial thermogenesis is increased 100% on a high-protein, low-fat diet versus a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet in healthy, young women. J Am Coll Nutr. 2002 Feb;21(1):55-61. Janet A Novotny, Discrepancy…
-
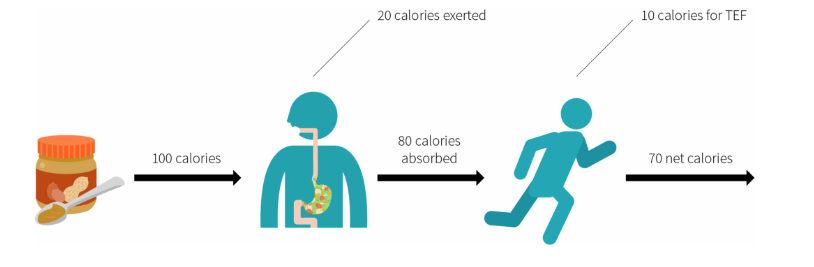
Do CALORIES Matter?
References: Andrea C, Is a calorie a calorie? Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79(suppl):899S–906S. Hall KD, Sacks G, Chandramohan D, Chow CC, Wang YC, Gortmaker SL, Swinburn BA. Quantification of the effect of…
-
Moon cycle Got You Craving??
In days 14-28 during the Luteal Phase of a woman’s cycle, food CRAVINGS may INCREASE. It may be beneficial for women to avoid being too restrictive with foods, increase fat intake, and…
-
Fructose, a killer??
Fructose’s unhealthy effects are rooted in rodent and human research where unrealistically high amounts of fructose are administered. Recent reviews have shown this to be a non issue in “normal” dietary intakes.…
-
Negative Calorie’ foods:
“‘Negative calorie’ foods (foods that have fewer calories than your body expends to digest them) likely don’t exist. However, food typically thought of as ‘negative calorie’ are often low in total calories…
-
How much protein can the body use in a single meal for muscle-building?
“Published! Our review of literature indicates that the amount of protein you can use for muscle-building purposes is larger than often claimed. We speculate that anabolism is maximized by spreading out protein…
-
Further Inspection: Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners in the past few years have been claimed in the media to promote weight gain. This idea stems deeply from observational research that find correlations between overweight and obese people…